Online Slope Calculator - Our 8 Free Tools
Our comprehensive suite of slope calculations will allow you to calculate a slope whether in percentage, degrees, radians, but also in all existing angle and slope units. Whether you need to calculate the slope of your roof, a ramp for accessibility, your terrain or a particular road, our tools cover a wide spectrum of use cases. No registration required, the calculation is performed 100% client-side, so in your browser, your data remains private.
Our 8 calculation modules
The basic slope calculator
It allows slope calculation from height and horizontal distance, or directly from an angle if you know it. You enter your elevation change and the distance traveled to get the slope percentage as well as the angle in degrees, radians, ratio and hypotenuse length.
The formula that will be used is relatively simple, it's the slope percentage which equals height over horizontal distance multiplied by 100: Slope (%) = (Height / Horizontal distance) × 100. Regarding angle θ: θ = arctan(Height / Distance). The calculator will automatically categorize the slope, classifying it from very gentle to extreme with examples of concrete applications.
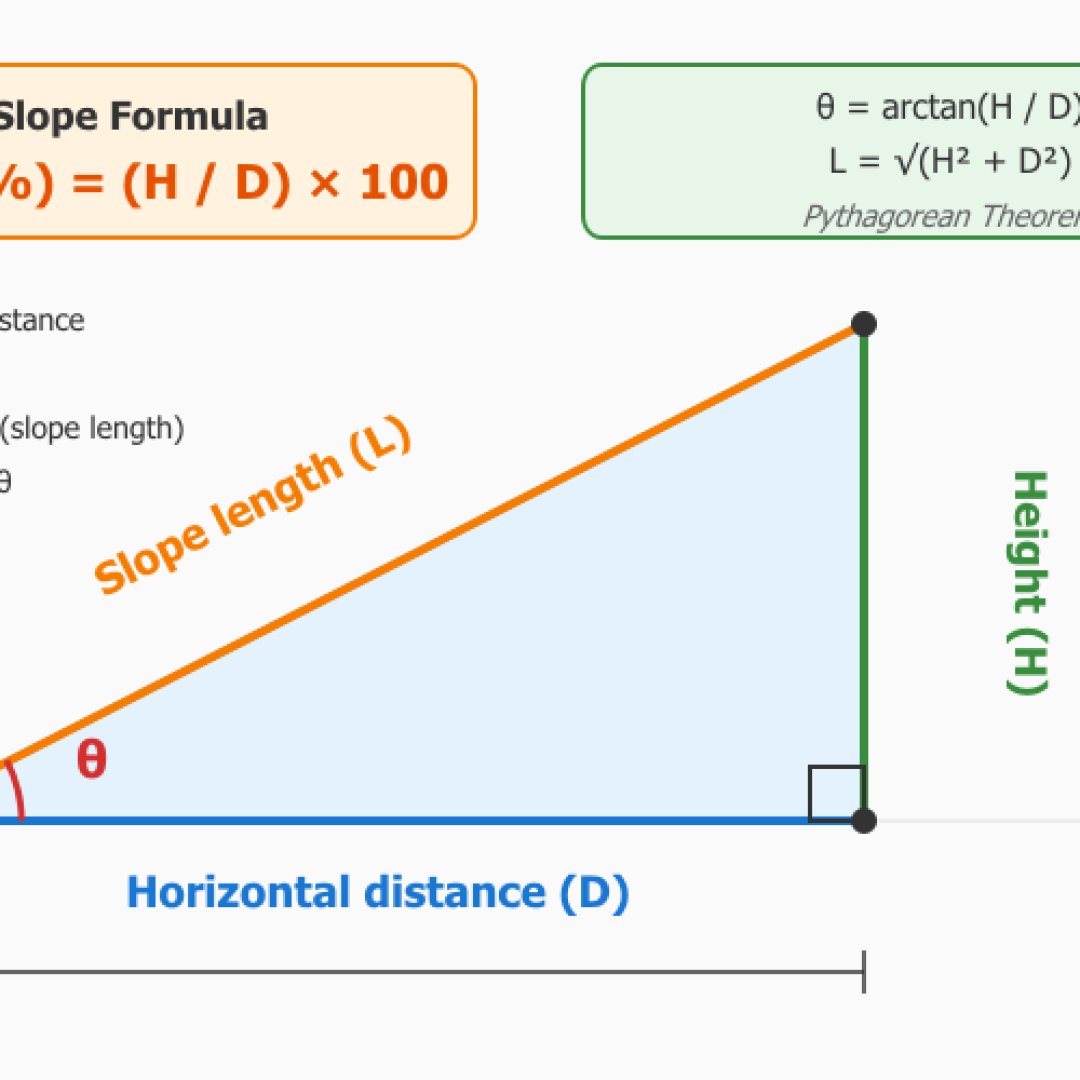
This module also allows you to perform the inverse calculation. That is, from a known angle and one dimension (horizontal distance, height or hypotenuse), it will determine the two other missing dimensions using fundamental trigonometric relationships.
The angular unit converter
The angular unit converter is comprehensive and allows you to switch from one unit to another in real time. It supports 10 types of units, whether percentage, degree, radians, gradians (used in surveying), turns (used for example in CSS), milliradians (ballistics), NATO mils (military), arc minutes and arc seconds (astronomy), and ratio (1:X).
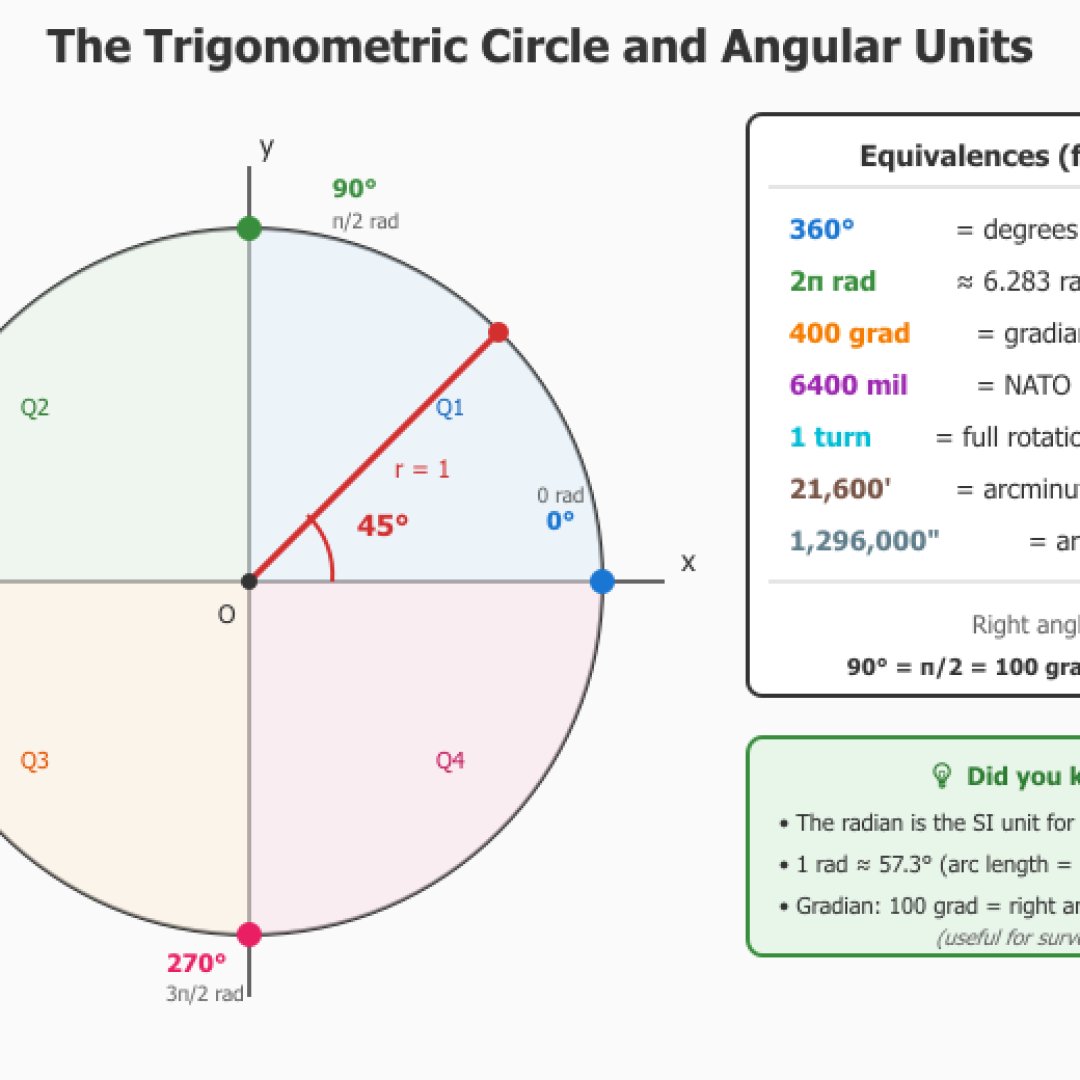
The dynamic visualization will display the trigonometric circle as well as the slope triangle to visually understand the relationship that exists between angle and inclination. Remarkable angles are automatically detected (hopefully ^^) and display their notation in π (for example π/4 rad for 45°).
Distance and midpoint calculation
This module allows calculating the Euclidean distance between two points in two dimensions or three dimensions. For three-dimensional calculation, it also determines the terrain slope between two altitudes, which can be useful in surveying as well as hiking.
The formulas are based on the Pythagorean theorem, demonstrated in Euclid's Elements (Book I, Proposition 47):
- 2D Distance = √[(x₂-x₁)² + (y₂-y₁)²]
- 3D Distance = √[(x₂-x₁)² + (y₂-y₁)² + (z₂-z₁)²]
- Midpoint = ((x₁+x₂)/2, (y₁+y₂)/2)
The 3D module also calculates the direction angles of the displacement vector relative to the three X, Y and Z axes, which can be useful in surveying and navigation but to be honest it's mostly useful at school!
Line equation (y = mx + b)
Allows generating a line equation from two points or from a slope and a point. This module provides three types of forms: slope-intercept (y = mx + b), point-slope (y - y₁ = m(x - x₁)) as well as standard form (Ax + By = C). It allows you to calculate the x-intercept, y-intercept and check if three points are collinear with ease.
Collinearity will be verified by calculating the area of the triangle formed by the three points. If the area is zero, the points are then aligned.
Interactive graphical visualization
Using a chart with the Chart.js library, it allows plotting your lines and points. You add lines by equation or coordinates. You control zoom from ±5 to ±100. You enable and disable grids. And you can export the result either as PNG image or SVG vector format which allows maintaining quality when enlarged.
Parallel and perpendicular lines
Allow you to find the equation of a parallel or perpendicular line passing through a given point. The mathematical rules are as follows: two lines are parallel if m₁ = m₂, perpendicular if m₁ × m₂ = -1. The integrated checker analyzes the existing relationship between two slopes and calculates the angle formed between two intersecting lines.
These properties derive directly from Euclidean geometry, fundamental notions in analytic geometry for studying lines in the Cartesian plane.
Linear regression
Will allow you to calculate the trend line using the least squares method by entering your data manually, either by pasting or importing them using a CSV file. The module will calculate the correlation coefficient R, the coefficient of determination R² as well as the standard error and residuals. Thus, you can make Y predictions for given X.
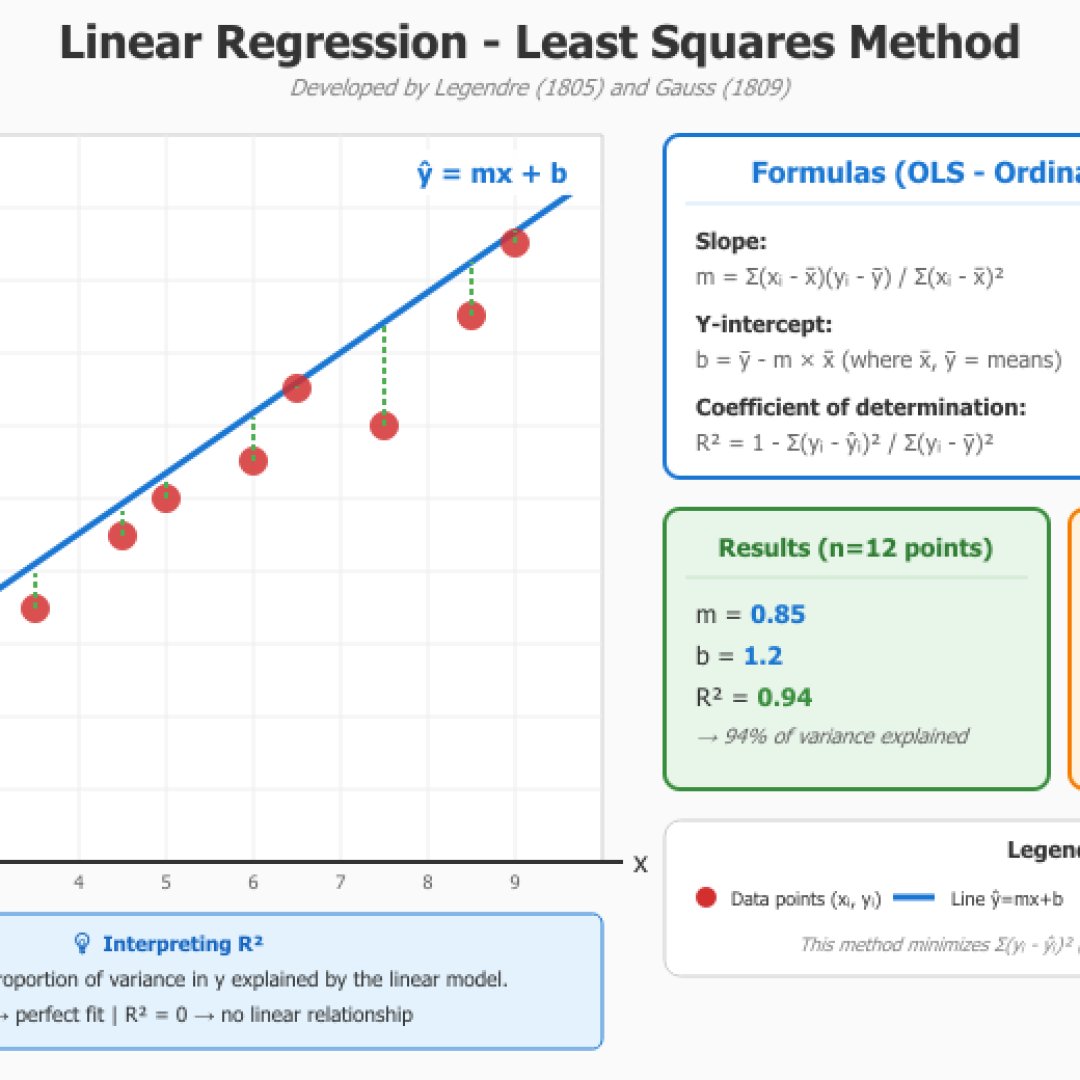
The least squares method was developed by Adrien-Marie Legendre (1805) and Carl Friedrich Gauss (1809), it minimizes the sum of squares of deviations between observed values and values predicted by the linear model.
Angles and elevation
You calculate elevation and depression angles for your projects, whether for example in ballistic shooting, pointing your telescopes at stars, calculating an aircraft climb angle or calculating a ramp slope for your construction activities. The inverse calculation allows finding the missing distance or height from a known angle.
This module accepts input angle in the 10 supported units, including directly as slope percentage.
Simply understanding slope calculation
Slope percentage
The slope percentage represents the ratio that exists between the elevation change and horizontal distance, all multiplied by 100. A 10% slope means that for 100 meters of horizontal distance, you will gain 10 meters of elevation. This is the standard format used on road signs and in construction.
Slope in degrees
The slope angle measures the inclination relative to horizontal. Thus, a 45-degree angle corresponds to a 100% slope (height equals distance). The conversion uses the tangent function: % = tan(angle) × 100.
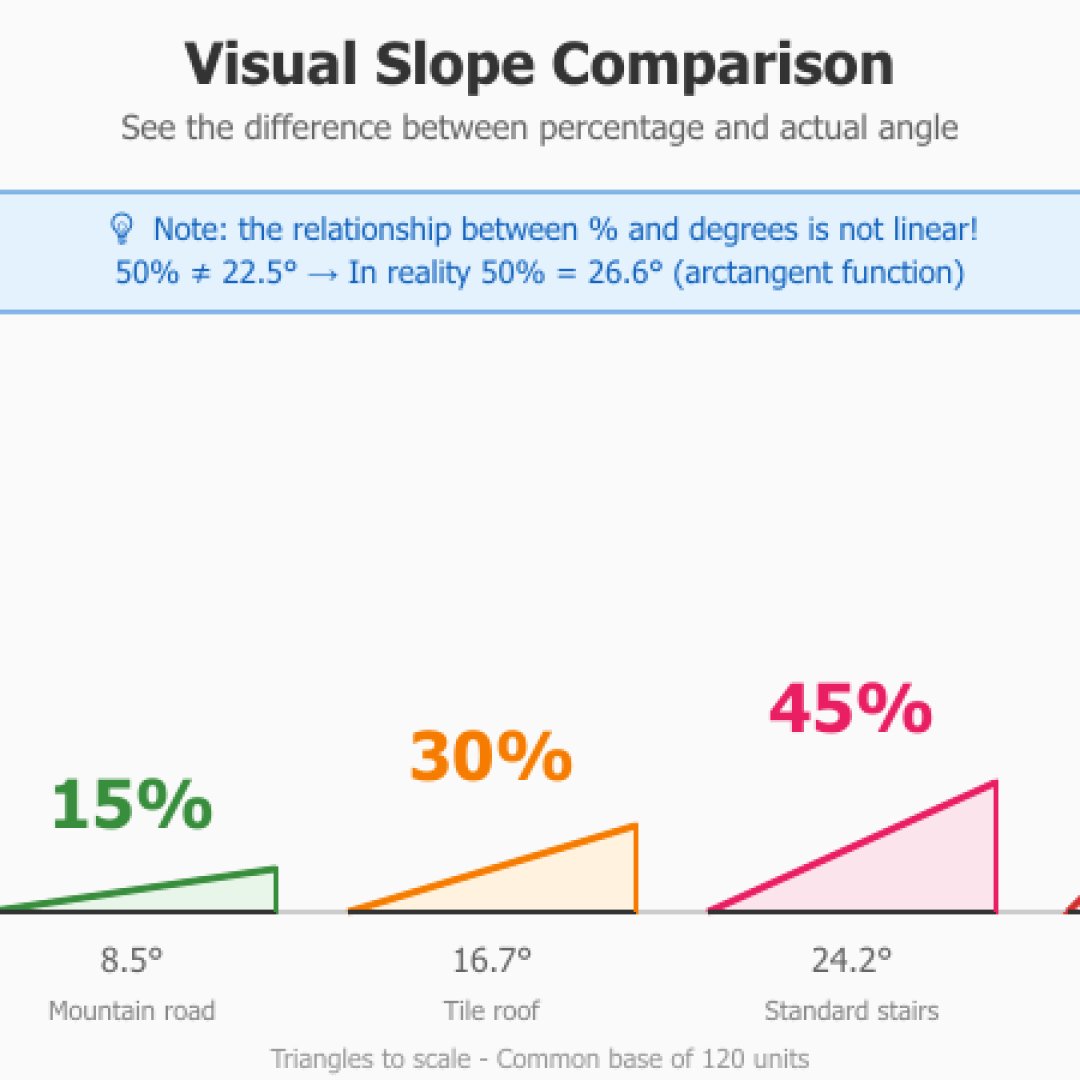
Common correspondences
| Percentage | Angle | Typical usage |
|---|---|---|
| 5% | 2.9° | Accessibility ramp (legal maximum) |
| 10% | 5.7° | Bike path, driveway |
| 15% | 8.5° | Mountain road |
| 30% | 16.7° | Gentle stairs, low-pitch roof |
| 45% | 24.2° | Standard stairs |
| 100% | 45° | Maximum walkable slope |
Practical applications
Roof slope calculation
The roof slope necessarily influences the choice of roofing materials as well as rainwater runoff. Flat roofs generally require a 5% minimum to ensure water drainage. Tile roofs generally require 15 to 35% depending on the type of tile (mechanical tiles, canal tiles or slates). Snowy mountain areas require steeper slopes of 35% to 60% to prevent roofs from collapsing in winter under snow weight.
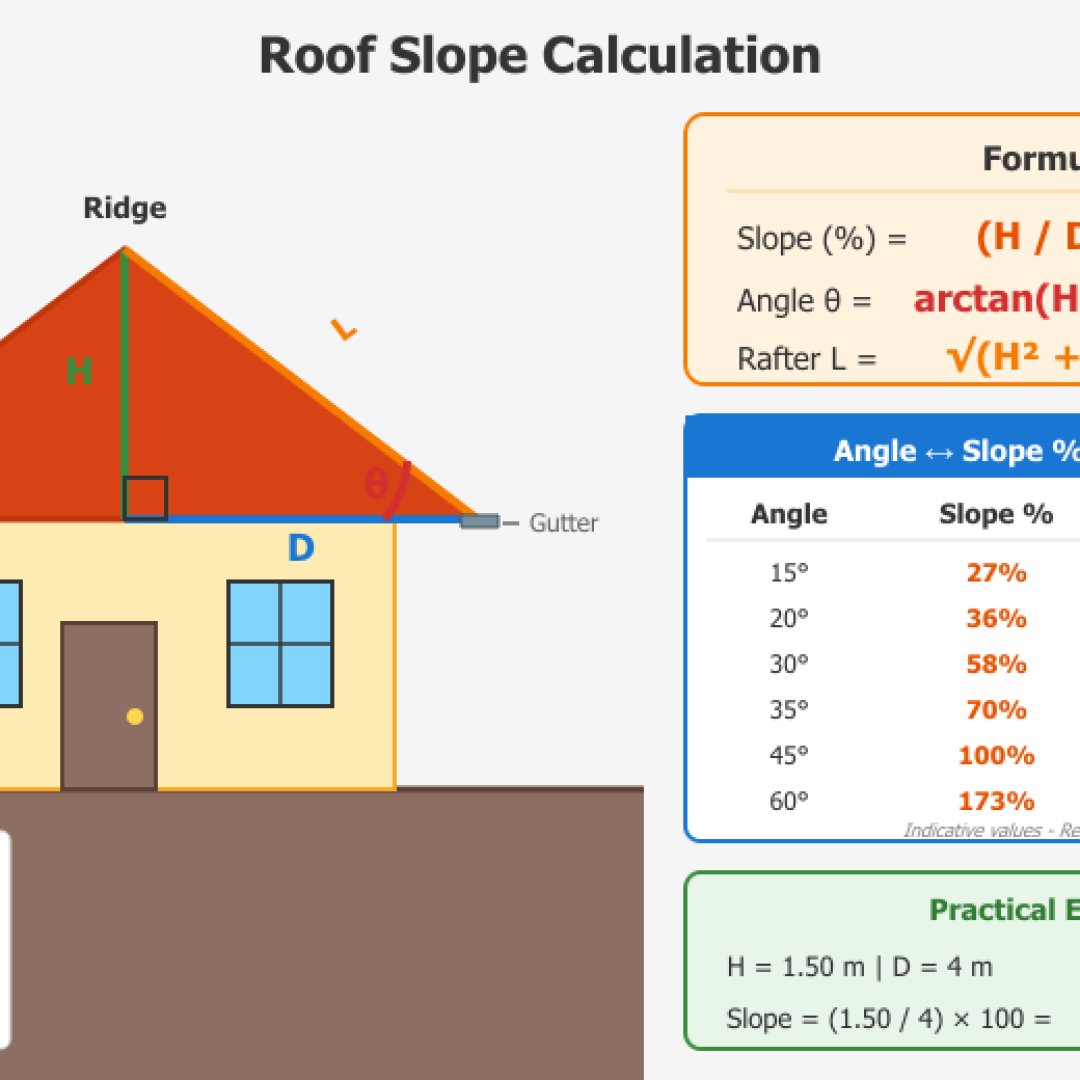
Thus, to calculate your roof slope, you must measure the gable height and horizontal distance (half the building width for a gable roof). Our small roof slope calculator gives the result in percentage and degrees.
Ramp for people with reduced mobility (PRM) and accessibility
French regulations impose a maximum slope of 5% for PRM (people with reduced mobility) access ramps. However, exemptions allow up to 8% over 2 meters maximum or 10% over 50 cm. Our calculator will verify compliance with your accessibility improvement project.
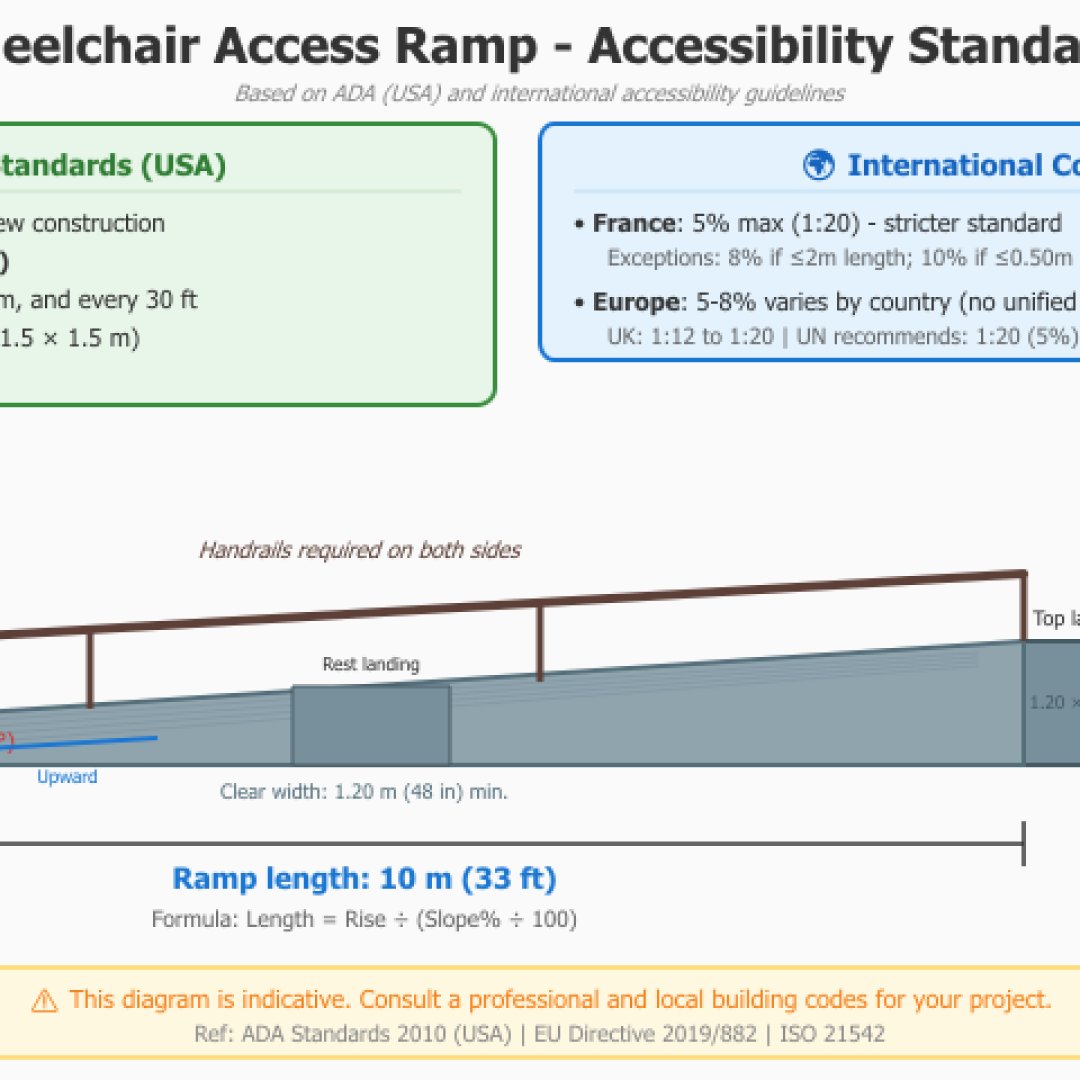
Reference: Decree of April 20, 2017 relating to accessibility for disabled persons in establishments receiving the public.
For comparison, American ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) regulations also impose a maximum ratio of 1:12 (i.e., 8.33%) for public access ramps.
Surveying and terrain
You should know that in surveying, slope is calculated between two measurement points at different altitudes. Contour lines on IGN maps allow determining elevation change (contour interval equals the altitude difference between two contour lines). Our small module calculates the actual terrain slope taking altitude into account.
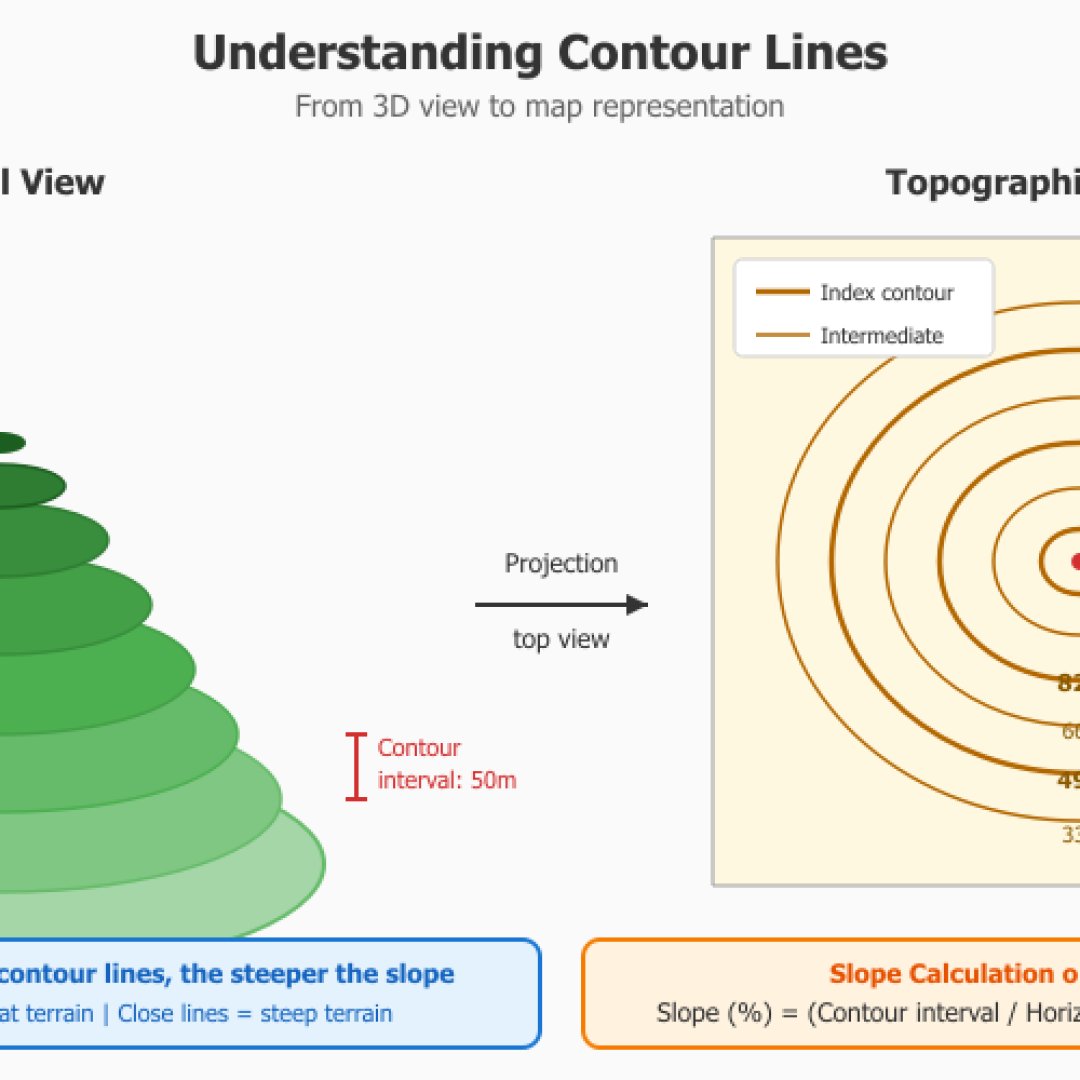
In professional surveying, the gradian (or gon) unit is often preferred because it divides the circle into 400 parts, which simplifies calculations (a right angle = exactly 100 grad), however in military context they often express in milliemes in the army and more in degrees at NATO level.
Framework and construction
Your timber frame calculation depends on the chosen slope. A roof consisting of one or two slopes requires rafters that will be dimensioned according to inclination and span. The slope length (which corresponds to the hypotenuse) determines the quantity of roofing materials needed for your project.
Reference formulas
Slope percentage calculation
Slope (%) = (Height / Horizontal distance) × 100Percentage to degrees conversion
Angle (°) = arctan(Slope% / 100) × (180 / π)Degrees to radians conversion
Radians = Degrees × (π / 180)Slope length (Pythagorean theorem)
Length = √(Height² + Distance²)Trigonometric relationships
tan(angle) = Height / Distance = Slope% / 100
sin(angle) = Height / Hypotenuse
cos(angle) = Distance / HypotenuseAngular unit conversions
Gradians = Degrees × (400 / 360)
NATO Mils = Degrees × (6400 / 360)
Arc minutes = Degrees × 60
Arc seconds = Degrees × 3600
Turns = Degrees / 360
Milliradians = Radians × 1000Line equation
Slope-intercept form: y = mx + b
Point-slope form: y - y₁ = m(x - x₁)
Standard form: Ax + By = CLinear regression (least squares method)
Slope (m) = [n∑xy - ∑x∑y] / [n∑x² - (∑x)²]
Y-intercept (b) = ȳ - m × x̄
R² coefficient = 1 - [∑(y - ŷ)² / ∑(y - ȳ)²]Euclidean distance
Distance 2D = √[(x₂-x₁)² + (y₂-y₁)²]
Distance 3D = √[(x₂-x₁)² + (y₂-y₁)² + (z₂-z₁)²]Parallel and perpendicular lines
Parallel: m₁ = m₂
Perpendicular: m₁ × m₂ = -1Angular units: reference guide
| Unit | Symbol | Complete circle | Main usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Degree | ° | 360° | Geometry, construction, navigation |
| Radian | rad | 2π ≈ 6.283 | Mathematics, physics, engineering |
| Gradian | grad | 400 grad | Surveying, geodesy (Europe) |
| Turn | turn | 1 turn | Programming (CSS), robotics |
| Milliradian | mrad | ~6283 mrad | Ballistics, optics, rifle scopes |
| NATO Mil | mil | 6400 mil | NATO military applications |
| Arc minute | ′ | 21 600′ | Astronomy, maritime navigation |
| Arc second | ″ | 1 296 000″ | High precision, GPS coordinates |
The radian is the angle unit of the International System (SI), defined by the BIPM in the SI Brochure. It corresponds to the central angle that intercepts an arc of length equal to the circle's radius (Imagine a circle: it's the central angle that cuts out an arc (a portion of the circumference) exactly the same length as the circle's radius. It's like unrolling the radius along the circle's edge to form this basic angle!).
Frequently asked questions
How to calculate a slope in percentage?
You simply divide the height (elevation change) by the horizontal distance. Then you multiply everything by 100. For example, 5 meters of elevation change over 50 meters of distance corresponds to 10% slope. Our tool allows you to perform this calculation automatically.
What's the difference between percentage and degrees?
On one side, percentage represents a ratio corresponding to height divided by distance multiplied by 100, and degrees measure the geometric angle. The relationship is not linear. That is, 100% equals 45 degrees. But 50% will not be 22.5 degrees. In reality it's 26.6 degrees. This non-linearity comes from the arctangent function (perfect for impressing at parties) used for conversion.
How to calculate roof slope?
You must measure the ridge height from the gutter level and the horizontal distance to the measurement point. Then, use our roof slope calculator to get the percentage and verify compatibility with your covering, whether tiles, slates or metal sheets.
What slope for a steel deck roof?
Steel decking accepts lower slopes, generally from 5% (3 degrees), according to DTU recommendations. Lower slopes require reinforced waterproofing for your project.
Reference: NF DTU 40.35 - Covering with corrugated sheets from coated steel sheets (AFNOR).
How to measure slope on terrain?
Simply. If you're equipped, use a rotary laser level, clinometer or smartphone app with accelerometer. And for large distances, you record altitude at two points, either with a GPS system that allows altimetric surveying, or simply calculate it from your position using a topographic map. And you measure the horizontal distance traveled.
What is the R² coefficient in linear regression?
The coefficient of determination R² indicates the proportion of data variance that is explained by the linear model. An R² of 0.95 means that 95% of data variation is explained by the regression line. The closer R² is to 1, the better the model fit.
Why use our calculator?
Our slope calculation suite offers you 8 complementary modules that cover maximum existing needs, from simple percentage calculation to advanced linear regression that gives you a headache. The interface allows you to perform your calculations simply from your mobile phone, tablet or computer. Know that all calculations are performed from your browser, for maximum speed and guarantee total confidentiality of the data you submit.
We tried to make maximum angular units available for everyone, in the same place (degrees, radians, gradians, percentages, ratios, milliradians, NATO mils, arc minutes and seconds and turns). Normally, they meet the needs of construction professionals, surveying, ballistics, astronomy and studious students.
Calculate your slope now with our free tools.